Machine learning generates pictures of proteins in 5D
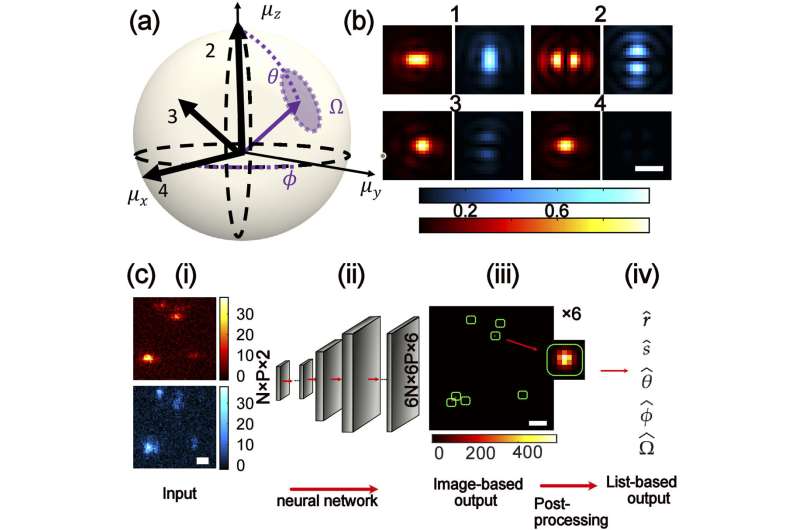
By combining machine learning with the laws of physics, researchers in the lab of Matthew Lew, associate professor of electrical and systems engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, have been able to sort out the orientation and position of overlapping single molecules in 5D from a single image.
Their research was published Sept. 26 in the journal Optics Express.
The five dimensions in question aren’t new or hidden spatial dimensions. Instead, a team headed by Tingting Wu, a Ph.D. student in the McKelvey School of Engineering’s imaging sciences program, was able to design a system that could tell the orientation of a molecule in 3D space as well as its position in 2D: five parameters from a single, noisy, pixelated image.
To wrest this additional complex information from a seemingly simple spot of light, the team did design a machine learning algorithm, but added an extra step.
“A lot of people use AI end-to-end,” Wu said. “Just put in the thing you have and ask the neural network to give you the thing you want.” She decided to break the problem into two steps to lighten the load on the algorithm, making it more robust.
The kind of imaging carried out in the Lew lab—of single molecules—tends to be very “noisy,” containing “specks” or fluctuations that can obscure an image. For most machine learning neural networks, Lew said, “robustly dealing with that kind of noise can be very complicated to learn.”
Humans, however, have already learned how signals from the molecules of interest and this noise are combined together within microscope images. Instead of asking the algorithm to re-learn the laws of physics, the team added a second “post-processing” algorithm–a straightforward computation that applied these physical laws to the results from the first algorithm.
“It’s like I’ve separated two problems into two algorithms,” Wu said.
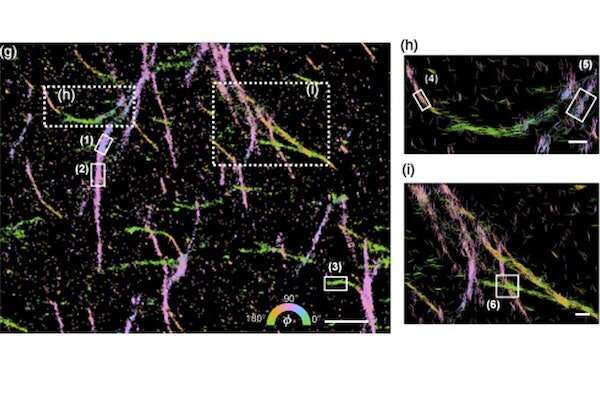
After processing thousands of snapshots, the result, Wu said, is a “beautiful image” that uses color, curvature and direction to indicate how thousands of molecules are connected to each other.
Ultimately, this system will be able to help researchers better understand biological processes at tiny scales—like the way in which amyloid proteins assemble to form the tangled structures associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Tingting Wu et al, Deep-SMOLM: deep learning resolves the 3D orientations and 2D positions of overlapping single molecules with optimal nanoscale resolution, Optics Express (2022). DOI: 10.1364/OE.470146
Citation:
Machine learning generates pictures of proteins in 5D (2022, November 2)
retrieved 2 November 2022
from https://techxplore.com/news/2022-11-machine-pictures-proteins-5d.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Technology News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

