Model suggests a billion people could get safe drinking water from hypothetical harvesting device
A team of researchers from X–Alphabet’s “moonshot factory,” Google and the WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme, Division of Data, Analytics, Planning and Monitoring, UNICEF, has developed a model that shows that a hypothetical device that uses solar power to pull water from the air could potentially serve a billion people across the world. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes the factors that went into their model and its possible impact on the development of devices meant to meet the global challenge of providing safe drinking water to the people of the world.
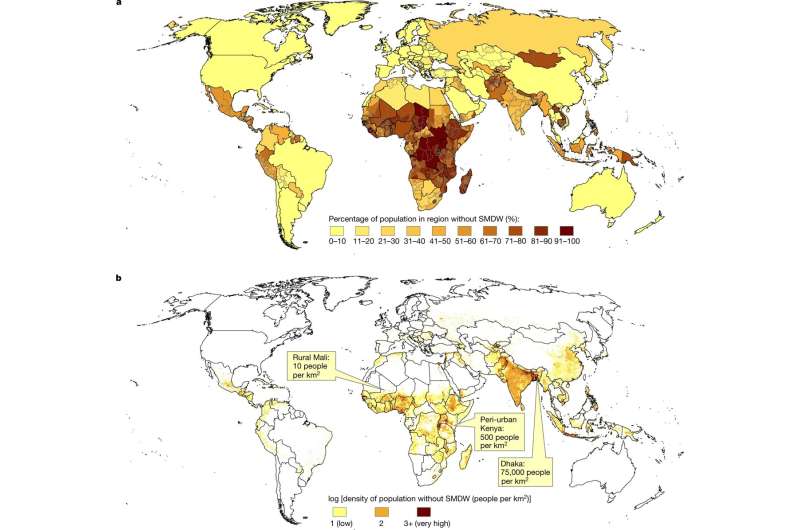
As the researchers note, approximately 2.2 billion people across the globe experience challenges in obtaining safe drinking water. This, they note, is despite efforts to build desalination plants in the most heavily impacted countries. As efforts to build more plants are undertaken, another approach might be taken to fill the need in the meantime—using small portable devices that pull water from the air using solar power. The team at Alphabet is currently working on such a device but has found it difficult to meet its goal of producing water at just one cent per liter. Their current model has thus far reached ten cents a liter. Recently they made the project open source hoping for creative ideas from others outside their area.
In building their model, the researchers acknowledged that solar powered devices capable of pulling water from the air only work well under certain conditions—where humidity levels regularly reach 30%, where there is plenty of sunshine and where it is warm enough. To account for people living in areas with such conditions, the researchers pulled average weather data from sites across the globe and mapped them with populations facing water challenges. In doing so, they found that more than a billion people could benefit from such a device that could produce on average five liters of drinking water per day. They conclude by claiming that current technology trends suggest that the hypothetical device they envisioned in their model could very soon become reality. At that point, however, it would fall to those who are able to pay for and distribute them to do so.
Jackson Lord et al, Global potential for harvesting drinking water from air using solar energy, Nature (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03900-w
© 2021 Science X Network
Citation:
Model suggests a billion people could get safe drinking water from hypothetical harvesting device (2021, October 29)
retrieved 29 October 2021
from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-10-billion-people-safe-hypothetical-harvesting.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Technology News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

